Feature Demonstrations
Discover the most advanced Gluon v2 features that automate your AI workflow and save time.
Auto Select - Automatic File Selection
Let AI select appropriate files based on task description
How does it work?
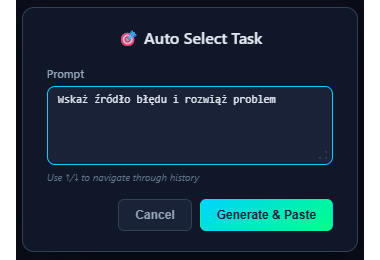
- Describe task in Quick Task field (e.g. "Fix login bug")
- Click Auto Select button
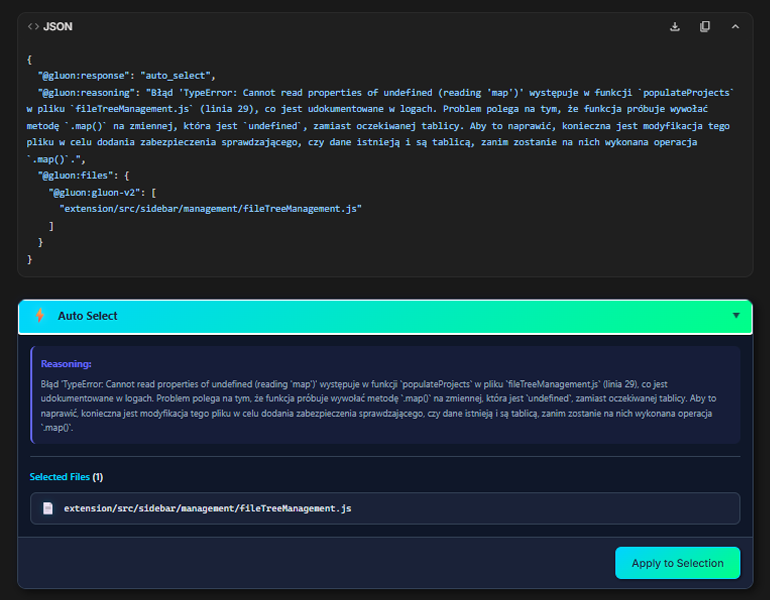
- Gluon sends project structure + description to AI
- AI analyzes and suggests files
- Overlay with suggestions appears
- Click "Apply" to automatically select all
❌ Before Auto Select
Manual file tree browsing, guessing which files are needed, wasting 1-3 minutes per task
✅ After Auto Select
AI automatically selects all needed files in seconds, zero guessing, instant work start
Step 1: Describe task
Step 2: AI suggests files
💎 Benefits
- ⚡ Time saving: 1-3 minutes saved per task
- 🎯 Precision: AI selects files more accurately than human
- 🧠 Context understanding: AI understands file dependencies
- 💡 Learning: See which files AI considers relevant
Context Save - Saving Context
Never lose perfect file configuration
How does it work?
- Select files for specific task
- Click Context Save button
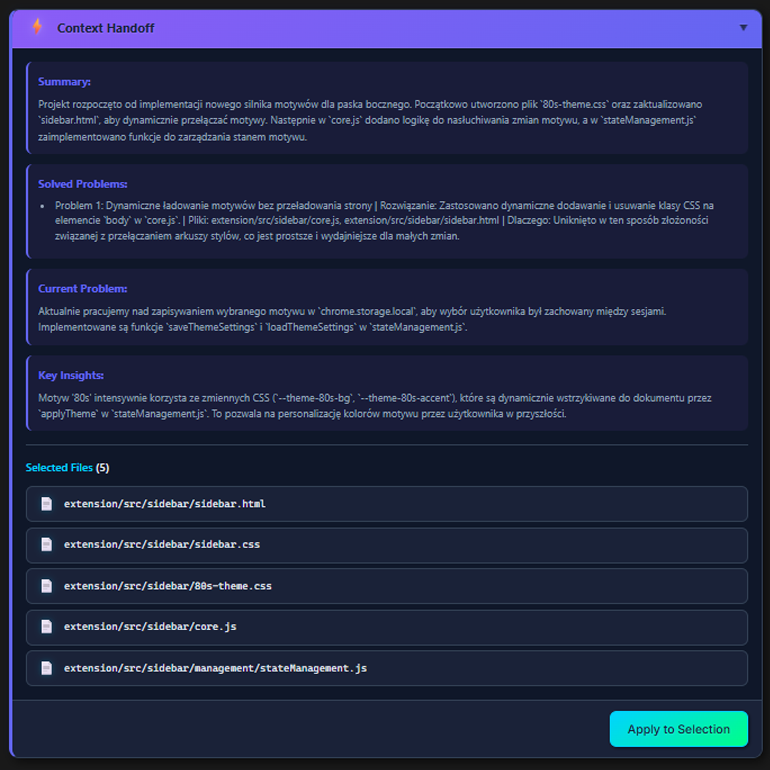
- AI generates summary of what you're doing
- Context saves with name, files and environment
❌ Without Context Save
Working on a bug for 2 hours. AI limit ends. Next day: "What was I doing? Which files? Where was I?"
Another 30 minutes to recreate context...
✅ With Context Save
Click Context Save. AI saves: what you did, which files, what you fixed, what's left.
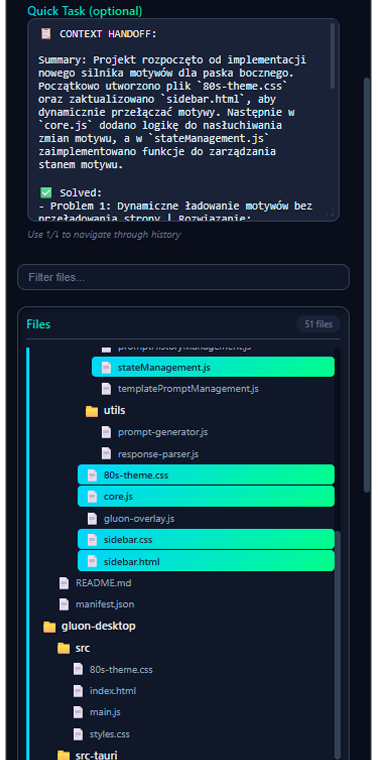
Next day: click tile → new AI session has FULL context. Start in 5 seconds.
AI generates name and summary
List of saved contexts
Prompt Generator
Optimize AI communication
How does it work?
- Select files and describe task generally
- Click Prompt Generator
- AI analyzes selected code and task
- Generates optimized, detailed prompt
- Gluon prepares ready context package
❌ Your Prompt
"Napraw błąd logowania"✅ Generated Prompt
"Based on the provided files (auth.js, login.component.ts, api.service.ts),
analyze the login flow and identify the bug causing authentication
failures. Specifically:
1. Check token validation in auth.js line 45-60
2. Verify API endpoint call in api.service.ts
3. Examine error handling in login.component.ts
4. Suggest fix with code examples"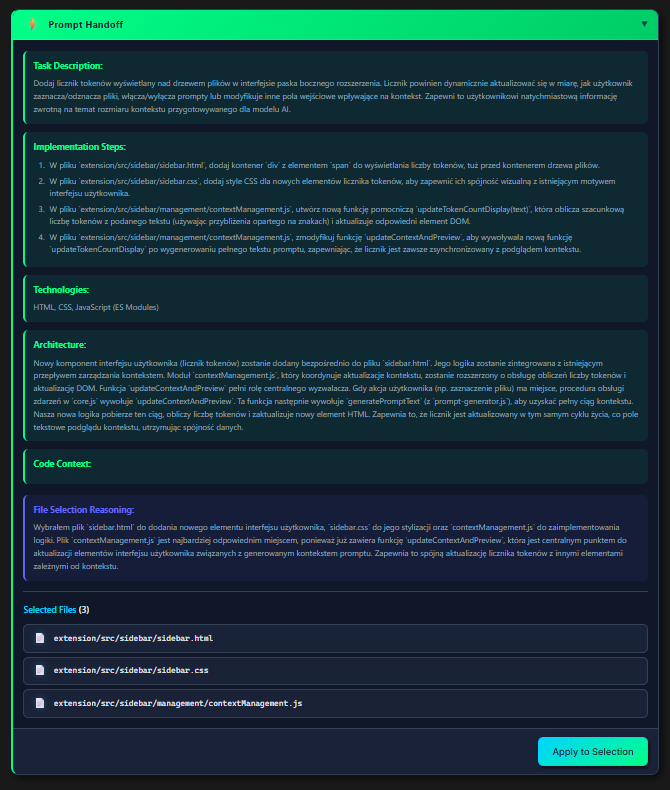
AI generates optimized prompt
💎 Benefits
- 🎯 Better answers: Detailed prompt = more precise AI responses
- ⚡ Token saving: AI understands context immediately without follow-ups
- 📚 Learning: See how to write good prompts
- 🚀 Speed: No "AI didn't understand → clarify" iterations
Template Configuration
Precisely control how AI processes your code
What are templates?
Templates define AI function behavior - Auto Select, Context Handoff and Prompt Handoff. Each template is a set of instructions on how AI should analyze and format results.
❌ Without Custom Template
AI uses default instructions. Results are generic, no project-specific details.
✅ With Custom Template
AI works by your rules. Understands project architecture, uses proper formats, generates precise results.
🎯 Configuration Fields
Basic:
- Template Name: Template name (e.g., "React Spec Generator")
- Template Type:
• Auto Select - file selection
• Context Handoff - context transfer between sessions
• Prompt Handoff - prompt generation - Role / Behavior Definition: Defines AI role (e.g., "You are a React architect, specializing in Next.js and TypeScript")
📝 Dynamic Fields - Context Handoff:
Context Handoff allows transferring full work context to a new AI session. Define how AI should summarize your work so far.
summary - Work history summary
Purpose: Defines how AI should create a chronological summary of the entire work session - what you did, in what order, what decisions you made.
How to use: Use instructions like "Create chronological history of all actions in this session, including decisions made and their reasons." When you move to a new AI session, you'll get full context of what happened.
Example value: "Present detailed work chronology: what I did step by step, which files I modified, what problems I encountered and how I solved them."
solved_problems - Solved problems
Purpose: Specifies how AI should describe problems you've already solved in this session.
How to use: Ask AI to list each bug/problem with solution description. This prevents duplicate work - new AI session knows what's already working.
Example value: "List of problems I fixed: problem name, cause, applied solution, files I changed."
current_problem - Current status
Purpose: Describes what you're currently working on and what's left to do.
How to use: AI in new session immediately knows where to continue. Instead of "what was I doing?" you have a ready starting point.
Example value: "Describe current problem I'm working on: what I'm trying to achieve, what I've already done, what blocks further progress."
key_insights - Key insights
Purpose: Gathers important technical discoveries from session - how code works, hidden dependencies, architecture.
How to use: AI saves project knowledge gained during work. In new session you use this knowledge instead of rediscovering everything.
Example value: "List of key technical discoveries: how architecture works, what dependencies exist between modules, what patterns are used."
📝 Dynamic Fields - Prompt Handoff:
Prompt Handoff analyzes your code and general task description, then generates detailed, optimized prompt for the next AI session.
task_description - Task goal description
Purpose: Defines how AI should describe the main task goal - what exactly you want to achieve.
How to use: Transform general "fix bug" into detailed description with context. AI in new session immediately understands WHY you're doing this task and WHAT is the expected result.
Example value: "Based on selected files and my task description, describe in detail the goal: what needs to be implemented, what problem to solve, what's the business context."
implementation_steps - Implementation plan
Purpose: Specifies implementation plan format - how AI should break down task into specific steps.
How to use: Instead of guessing "what to do next", you have a ready list of atomic steps. Each step is a concrete action you can execute.
Example value: "Create implementation plan: atomic steps (one file/one function), in logical order, with dependencies between steps."
technologies - Technology stack
Purpose: Describes how AI should list technologies, libraries, and tools used in the task.
How to use: AI in new session knows what technologies are involved. Thanks to this, it suggests solutions compatible with project stack, doesn't propose tools you don't use.
Example value: "List all technologies used in selected files: framework, libraries, build tools, versions if relevant."
architecture - Architecture and flow
Purpose: Defines how AI should describe application architecture and data flow in task context.
How to use: AI understands how components work together. Instead of "change file X", AI sees "change file X, which will affect Y and Z".
Example value: "Describe architecture: how components are connected, how data flows, what are integration points."
code_context - Code context
Purpose: Describes how AI should explain code context that is NOT attached to task, but is relevant.
How to use: Sometimes you don't want to send 50 files, but AI should know they exist. This field allows AI to describe "what's out of view" - external APIs, services, modules that code interacts with.
Example value: "Describe context of code not attached to task: external APIs we use, backend services, modules we integrate with."

